In clinical diagnostics and laboratory medicine, proper blood sample collection is essential for obtaining accurate and reliable test results. The non vacuum tube is a widely used blood collection device designed to support controlled and gentle blood handling. Unlike vacuum tubes that rely on preset negative pressure, a non vacuum tube allows healthcare professionals to manually manage blood transfer, offering enhanced flexibility in patient-centered care. Non vacuum tubes are commonly used in hospitals, diagnostic laboratories, outpatient clinics, and point-of-care environments where patient safety, sample integrity, and procedural control are critical.
What Is a Non Vacuum Tube?
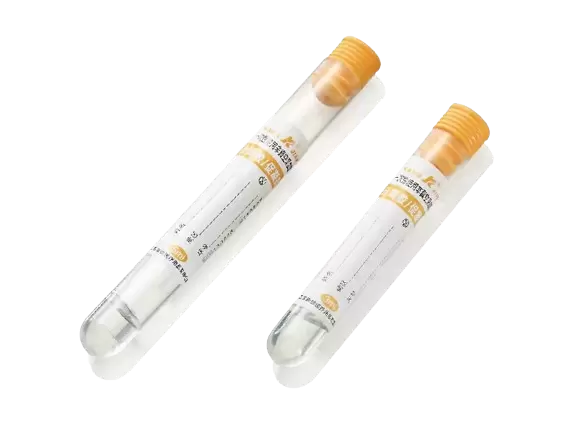

A non vacuum tube is a blood collection tube that does not contain internal negative pressure. Blood is typically drawn using a syringe and then transferred into the tube manually. This design allows clinicians to control the speed and volume of blood entering the tube, reducing mechanical stress on blood cells.
Non vacuum tubes are usually manufactured from medical-grade materials such as polypropylene, ensuring chemical stability, transparency for visual inspection, and compatibility with automated laboratory analyzers. Depending on the intended diagnostic use, a non vacuum tube may contain anticoagulants (such as EDTA, heparin, or sodium citrate), clot activators, or no additives at all.
All non vacuum tubes intended for clinical use are designed to comply with applicable medical device and in-vitro diagnostic (IVD) standards, ensuring safety, sterility, and consistent performance.
Key Clinical Benefits of Non Vacuum Tubes
Enhanced Control During Blood Collection
One of the most significant advantages of a non vacuum tube is the ability to manually regulate blood flow during sample transfer. This controlled collection process is particularly valuable for patients with small, fragile, or difficult veins, where automatic vacuum pressure may lead to vein collapse or unsuccessful blood draws.
By allowing healthcare professionals to adjust collection speed in real time, a non vacuum tube supports a smoother and more predictable blood transfer process. This level of control is especially important for tests that require precise blood-to-additive ratios, as even small deviations can affect test validity. As a result, non vacuum tubes contribute to both patient safety and analytical accuracy.
Improved Patient Comfort and Safety
Patient comfort plays an increasingly important role in clinical care, especially for individuals who require repeated blood testing. The use of a non vacuum tube minimizes sudden pressure changes during blood collection, which can otherwise cause discomfort, bruising, or vascular trauma.
This gentle collection method is particularly beneficial for pediatric patients, elderly individuals, and patients undergoing long-term treatments such as chemotherapy or dialysis. By reducing pain, stress, and tissue damage, non vacuum tubes help create a more patient-friendly blood collection experience while maintaining clinical effectiveness.
Reduced Risk of Hemolysis and Sample Degradation
Hemolysis is a common pre-analytical issue that can compromise laboratory results and lead to sample rejection. Excessive vacuum pressure is a known contributor to red blood cell damage. A non vacuum tube enables gradual and controlled blood transfer, helping preserve cell integrity and biochemical stability.
Lower hemolysis rates result in fewer repeat collections, reduced laboratory workload, and improved turnaround times. For this reason, non vacuum tubes are particularly suitable for sensitive hematology, biochemistry, and immunoassay testing where sample quality is critical.
Operational Flexibility Across Healthcare Settings
A non vacuum tube does not require specialized vacuum holders or dedicated blood collection systems, making it highly adaptable across a wide range of healthcare environments. These tubes are especially useful in emergency departments, bedside testing scenarios, mobile clinics, and field healthcare operations where equipment availability may be limited.
Additionally, the absence of internal vacuum simplifies storage and transportation, as there is no risk of vacuum loss over time. This practical advantage makes non vacuum tubes a reliable and versatile solution for diverse clinical workflows.
Medical Applications of Non Vacuum Tubes
Pediatric and Geriatric Blood Collection
In pediatric and geriatric care, venous access is often challenging due to smaller vein size or increased fragility. A non vacuum tube allows clinicians to collect blood slowly and precisely, minimizing trauma while still obtaining sufficient sample volume for diagnostic testing. This controlled approach helps reduce procedural stress for vulnerable patient populations and supports consistent diagnostic outcomes in age-sensitive clinical settings.
Specialized and Low-Volume Diagnostic Testing
Certain laboratory tests require strict control over sample volume or involve limited blood availability. Non vacuum tubes provide greater flexibility for low-volume sampling, making them suitable for specialized biochemical, immunological, and hematological analyses. By enabling precise blood transfer, a non vacuum tube helps maintain correct additive ratios, which is essential for test reproducibility, accuracy, and compliance with laboratory protocols.
Emergency and Point-of-Care Scenarios
In emergency medicine and point-of-care testing, speed, adaptability, and simplicity are essential. A non vacuum tube allows rapid blood sample handling without the need for complex or bulky equipment, supporting timely clinical decision-making in urgent situations. These tubes are commonly used in ambulances, emergency rooms, and bedside testing environments where reliability and ease of use are critical.
Key Considerations When Choosing Non Vacuum Tubes for Medical Use
Proper Training and Technique
Because a non vacuum tube relies on manual blood transfer, correct technique is essential to ensure sample quality. Healthcare professionals should receive proper training on filling methods, gentle mixing when additives are present, and safe handling practices to prevent clot formation, contamination, or sample loss.
Sterility and Regulatory Compliance
All non vacuum tubes used in clinical settings must meet relevant regulatory and quality requirements. Tubes should be sterile, clearly labeled, and manufactured under controlled conditions to ensure patient safety and diagnostic reliability.
Compliance with international medical device and IVD regulations ensures that non vacuum tubes are suitable for routine clinical and laboratory use.
Sample Handling and Laboratory Accuracy
After collection, blood samples in a non vacuum tube should be processed promptly and stored under appropriate conditions. Strict adherence to laboratory protocols for transport, storage, and analysis helps maintain sample integrity and supports accurate diagnostic results.
Conclusion
The non vacuum tube is a vital component of modern blood collection systems, offering controlled sampling, improved patient comfort, and flexible application across a wide range of clinical settings. When selected appropriately and used in accordance with medical standards, non vacuum tubes support high-quality sample collection and reliable laboratory diagnostics, ultimately contributing to safer, more effective patient care.
https://www.kangene.com/Non-Vacuum-Blood-Collection-Tube/
www.kangene.com
Jiangsu Kangjian Medical Supplies Co., Ltd.